The carmaker’s advanced battery technology roadmap may be set to transform EVs for automotive manufacturing; enhancing power, range and efficiency.
Toyota has unveiled a striking battery technology roadmap that has the potential to impact the future of EVs through pioneering battery technologies. The initiative covers a range of innovative battery solutions, both liquid and solid-state, designed to enhance power, driving range, charging speed and cost-effectiveness, making it a crucial development for the automotive industry. The new battery technology will feature in the automaker’s upcoming models.
Liquid Electrolyte Battery Advancements
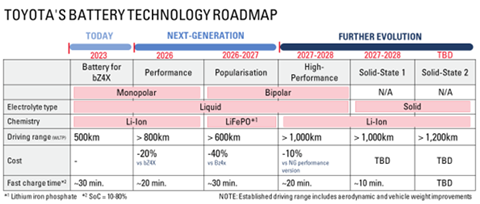
Toyota acknowledges that liquid electrolyte batteries currently dominate the EV market. To cater to the diverse needs of their customers and automotive manufacturing standards, the automaker has said it is committed to enhancing liquid electrolyte batteries in three key categories:
1. Performance Battery (Lithium-Ion)
Set to debut in next-generation Toyota EVs by 2026, the performance battery aims to extend EV boundaries by offering a driving range of over 800 km (497 miles). This innovation will be achieved, according to Toyota, by allowing for improved vehicle aerodynamics and reduced weight, accompanied by a 20% cost reduction compared to the current bZ4X EV. The Performance battery promises rapid recharging in just 20 minutes for SOC 10-80%, aligning with automotive manufacturing’s demand for efficiency.
2. Popularisation Battery (Lithium Iron Phosphate)
Beyond ranges, Toyota also recognises the importance of cost-effectiveness in automotive manufacturing. The carmaker is developing the Popularization battery, expected to enter the market in 2026-27. By employing bipolar technology combined with cost-efficient lithium iron phosphate (LiFePo), this battery will also offer a substantial 40% cost reduction compared to current models, and a 20% increase in driving range. Moreover, fast recharging in 30 minutes or less for SOC 10-80% ensures quick turnaround times on the production line.
3. High-Performance Battery (Lithium-Ion)
The carmaker’s High-performance battery, slated for introduction in 2027/28, wil deliver an impressive driving range of over 1,000 km (621 miles). According to Toyota, this will be achieved through a combination of bipolar structure, lithium-ion chemistry and a high nickel cathode. The high-performance lithium-ion battery will further reduce costs by 10% compared to the Performance battery, ensuring a competitive edge in the automotive manufacturing sector. Rapid charging in just 20 minutes for SOC 10-80% further aligns with production efficiency demands.
Solid-state battery innovations
Toyota recognises that while liquid electrolyte batteries have served EVs well, the promise of solid-state batteries has tantalised the industry for years. Its solid-state lithium-ion batteries “have a solid electrolyte that allows for faster movement of ions and a greater tolerance of high voltages and temperatures,” the company says. These qualities make the batteries suitable for rapid charging and discharging and delivering “power in a smaller form,” according to a company press release.
The carmaker has now made a significant breakthrough in solid-state battery technology, which it says eliminates previous concerns about battery life. The development has shifted the carmaker’s focus toward mass production, with the aim of commercial readiness in the next 4-5 years.
Toyota’s first solid-state battery is expected to transform EVs through an impressive 20% increase in driving range compared to the Performance battery, equating to 1,000 km (621 miles), and Lightning-fast charging in just 10 minutes or less for SOC 10-80%. The company is already advancing a higher-specification solid-state battery targeting a remarkable 50% improvement in cruising range compared to the Performance battery, promising even greater potential for automotive manufacturing.
Optimising battery height for enhanced performance
Battery innovations are never isolated and tend to have ramifications throughout the vehicle. An example would be that aerodynamics play a pivotal role in driving range optimisation for EVs, and Toyota has been taking it a step further by focusing on CdA; the product of drag coefficient and vehicle frontal area. The height of the battery is at the core of Toyota’s strategy.
By reducing battery height from the current 150mm to 120mm (and even down to 100mm for high-performance models), Toyota aims to lower the vehicle’s overall height. This, in turn, will significantly improve CdA, boosting the vehicle’s range performance—a crucial consideration for automakers looking to maximise their EV efficiencies.






































No comments yet