Protecting battery packs is the fundamental first step when designing the body-in-white for BEVs. We talk to SSAB’s Robert Ström about the Docol EV Design Concept and platforms for new AHSS solutions

What do you mean by ‘EV Concept?’
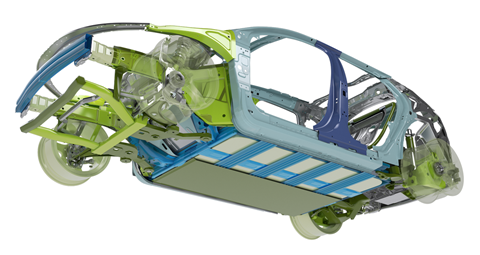
Robert Ström: As battery packs for BEVs get bigger, for longer range, a central challenge remains for automotive design engineers: how to protect the battery cells during a crash. That is, there can be no intrusion whatsoever into the cells – even for the very demanding side pole impact test. The EV Concept is a ‘virtual platform’ to foster innovative ideas and basic research on AHSS solutions for BEVs.
Can you provide an EV Concept example?
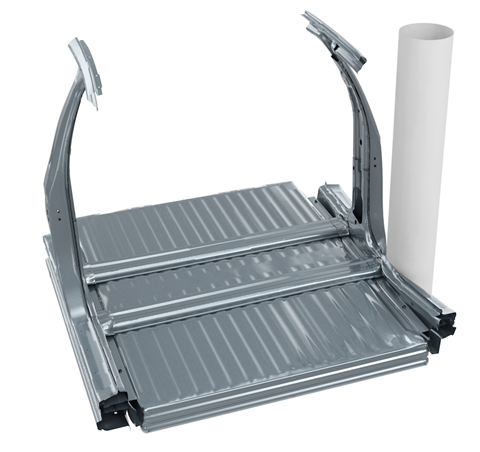
We’ve put together designs and initial prototypes for a unique AHSS battery enclosure with a bottom structure made from Docol 1700 Martensitic that is 3D roll-formed into beams then welded into a mesh pattern.

What is 3D roll-forming?
In a 3D roll-forming machine, the rollers can move in all directions while forming the steel. We’ve used 3D roll-forming to create a beam that is one part fixed and one part flexible. Then one beam can be placed perpendicularly to a similar profile – that is, turned upside down – without doubling its height in the Z-direction. This is key for BEV OEMs: if battery enclosures are tall, that either reduces space in the passenger compartment or creates a taller, less streamlined vehicle.
What are other advantages to this battery load-carrying design?
The mesh of 3D beams maintains a specified distance between the enclosure’s bottom plate and its battery tray, ensuring protection from impacts coming from below the car. And because the ‘grooves’ run along the length of each beam, the load paths in X and Y directions are unbroken and therefore the strongest possible.
What other designs makes this battery enclosure concept impact resistant?
A frame made from 1700M runs around the battery tray, providing impact protection as well as a stabilising structure. And the battery enclosure’s tray is made from steel, drawn to form completely vertical (90°) side walls that optimise the space for the battery pack. The tray also prevents the battery cells from leaking into the environment during and after a crash.
What is the estimated weight for the entire battery enclosure?
The lowest possible weight for the battery enclosure is 75kg. That’s for a battery pack that’s 1,742 x 1,320 x 120mm.
What are some other EV Concepts?
Unlike a car with an internal combustion engine, an EV must absorb more energy through the car’s sill. Why? The weight of the EV’s battery, the EV’s stiffer underbody, and the requirement that no intrusion whatsoever is allowed into the EV’s battery pack.
Isn’t extruded aluminium seen as an efficient way of absorbing higher energy levels?
Yes, but at a steep price premium compared to AHSS. We’ve tried to match the performance of extruded aluminium sill beams made from EN AW-6082 T6 with a thickness of 4.5mm for the outer walls and 3mm for its ribs. Accordingly, SSAB has run many, many simulations for numerous different profile designs for 2D roll-formed sill beams made from Docol CR 1700M steel. But, importantly, we adjusted the wall thickness for each 1700M profile so it would weigh the same as the 6082 T6 aluminium sill beam.
And what did you find out?
We found out that sill beam profile performs best: its crash performance is similar to that of an aluminium beam. And to repeat, the weights are the same for both materials: AHSS vs. aluminium.
Any prototype testing yet of the Docol 1700M sill beams?
Yes, initial prototype testing that is. They did well, but we need to perform more testing on the welding used to create the profile to discover if the welds are ductile enough to handle deformation without cracking.
What other EV concepts are in the works?
Well, the most efficient way of protecting the EV’s battery pack from intrusion during a side crash is to ensure that the cross-members directly underneath the floor of the passenger compartment do not deform. The cross-members must be strong and not absorb energy at all – instead, they should transfer the side crash force from one side of the car to its opposite side.

So have you experimented with different AHSS profiles for cross-members?
Yes, using Docol 1700M again. There is a huge performance difference between different profile designs. For example, while keeping all the beam profiles at the same weight, large radius beams perform best.
But don’t AHSS steels have very high yield points? So wouldn’t local buckling be a concern for these beams, with their wide radius and thin-walls?
Yes, but one way to restrain local buckling is to make the wide segments of a profile ‘less wide’ by means of a groove. Grooves provide more radii through which forces can travel. The simulation results show that an optimised cross-member can more than double the crash load transfer performance over the square-shaped profile. And what is critical for this cross member application is the peak load, not the energy absorption. In an event of a crash of a BEV, the peak load of the cross-members must not be exceeded.
What’s next for the EV Concept?
We want to appeal to OEMs’ self-interest, motivating them to use AHSS steels for critical components in battery electric vehicles – while achieving the same weight savings as higher-priced aluminium or other CO2-intensive materials. We also want OEMs to achieve higher levels of AHSS material utilisation so they can realise additional savings. We’ll provide auto designers with AHSS simulations, such as the side crash simulations, that show how to improve the performance of critical safety components, like improving the performance of floor cross members by a factor of two.
And finally we want to demonstrate innovative new designs and production methods for AHSS steels, such as 3D roll-forming for more space-efficient EV battery enclosures. Innovations like 3D roll-forming AHSS to fabricate cross meshes that work under compression will really open up the way designers think about achieving maximised axial load performance – both lateral and longitudinal.
To download the full AMS January-March 2020 digital magazine click here.






































No comments yet