Electric Dreams: Tesla’s gigafactory network and EV battery production blueprint
From Fremont to Berlin, Tesla’s gigafactories are the drivers in its goal to lead the EV market. Each site plays a crucial role in electric vehicle and battery innovation, ensuring Tesla meets global demand and maintains its lead in the electrification race.

If “EVs” and “Battery Production” doesn’t trigger “Tesla” for you, then your finger is not on the pulse. Tesla stands as a dominant force driving battery innovation and EV production scale; now, somewhat of a truism. But with fluctuating demand and multiple challenges hindering widespread EV adoption, Tesla’s strategy in current and planned vehicle production, battery technology advancements, and strategic expansions plays a leading role in the entire industry’s electric dreams.
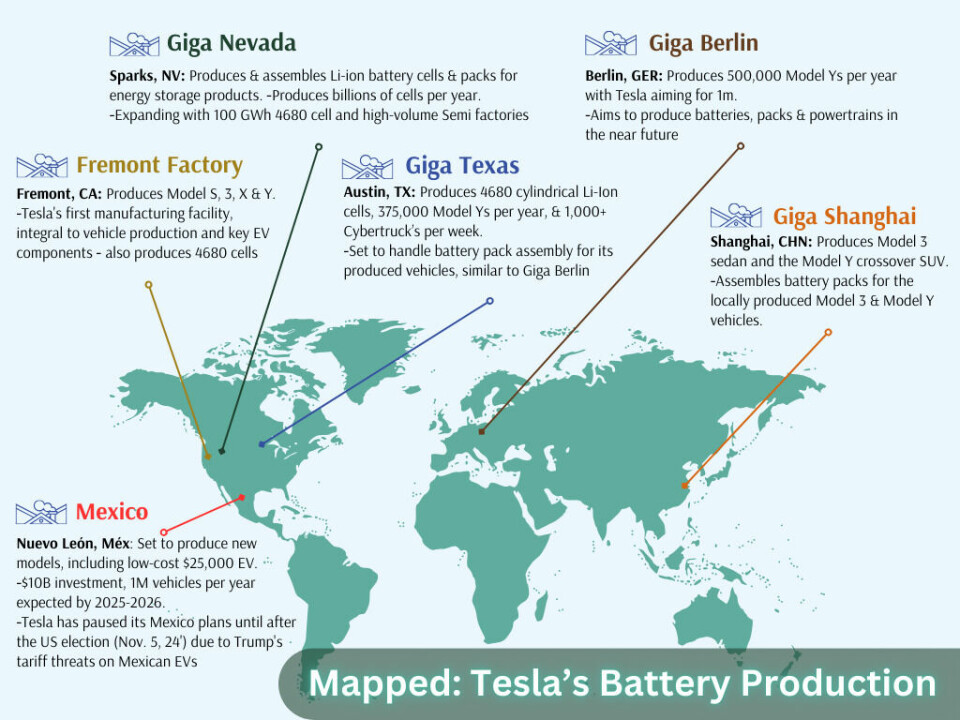
Tesla operates several key manufacturing sites globally, each integral to its ambitious production goals. These include Gigafactory Nevada, Fremont Factory in California, Gigafactory Shanghai in China, Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg in Germany, Gigafactory Texas in the United States, and Gigafactory New York.
Each facility serves as a production hub while supporting Tesla’s battery production distribution across key markets. Central to Tesla’s production capabilities are its diverse vehicle platforms and models, which range from the popular Model Y and Model 3 to the voguish Cybertruck and the flagship Model S and Model X.
“In 2023, we delivered over 1.2 million Model Ys, making it the best-selling vehicle, of any kind, globally. For a long time, many doubted the viability of EVs. Today, the best-selling vehicle on the planet is an EV”
The scalability and adaptability of these platforms allow Tesla to cater to varying consumer demands while maintaining innovation in design and technology.
In parallel, Tesla’s advancements in battery supply are critical. The company has been exploring various battery chemistries, including potential transitions to more cost-effective options like sodium-ion technology. The technological shift signals Tesla’s commitment to finding ways to reduce production costs and enhance the energy efficiency of its vehicles; crucial in meeting global demand amidst various disruptions and regulatory challenges.
By no means an exhaustive list, we take a closer look at the central nervous system vitalising Tesla’s EV and battery production network.
The Fremont Factory, California
Tesla’s Fremont Factory in California is key to the company’s entire automotive manufacturing blueprint. Acquired in 2010, Fremont is Tesla’s first and one of its largest facilities, producing key models like the Model S, Model 3, Model X and Model Y. With an annual capacity exceeding 650,000 vehicles, including over 550,000 Model 3 and Model Y units, it reached a milestone in May 2024 with its 3 millionth EV. Employing over 20,000 people, the facility is a key hub for electric motors, batteries and powertrains, integrating Tesla’s production processes tightly for quality and efficiency.
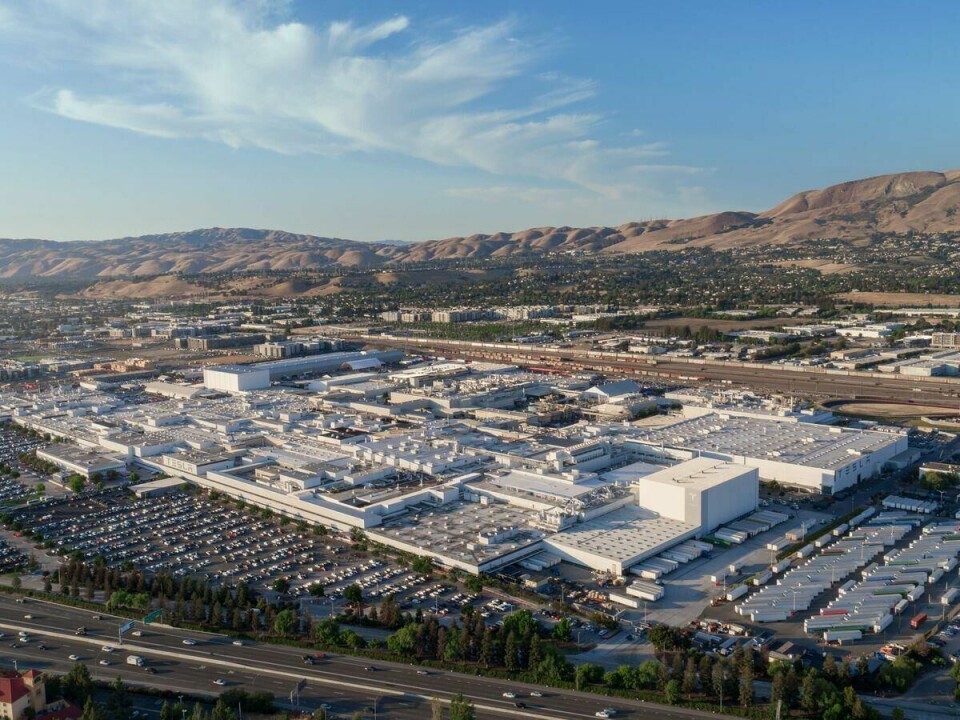

Since acquiring the factory from NUMMI (the Joint Venture between GM and Toyota) in 2010, the factory has played a crucial role in Tesla’s EV production milestones. It was the first facility to produce the aforementioned models.
The factory’s location in the South Fremont District, sat between the Warm Springs BART station and the California State Route 262, has also proven advantageous for logistics and transportation.
While Tesla only purchased 210 of the original 370 acres owned by NUMMI, Fremont’s expansive footprint has allowed for continuous growth and optimisation.
Despite intermittent challenges, such as fire incidents and environmental concerns, the Fremont Factory remains a critical component of Tesla’s manufacturing operations. As the company continues to push the boundaries of EV technology, this factory will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of EV and battery production.
”Before Tesla purchased the Fremont factory, the record output of the previous owner was nearly 430,000 vehicles made in a single year. In 2023, the Tesla Fremont factory produced nearly 560,000 vehicles”
The California Kato Factory
Tesla’s Kato Factory, eponymous with the street on which it’s located, also in Fremont, serves as a linchpin in the company’s pursuit of battery development and pilot production initiatives. Kato operates as a testing ground for Tesla’s latest battery technologies, enabling iterative refinement and optimisation of designs before scaling up production at its Gigafactories.
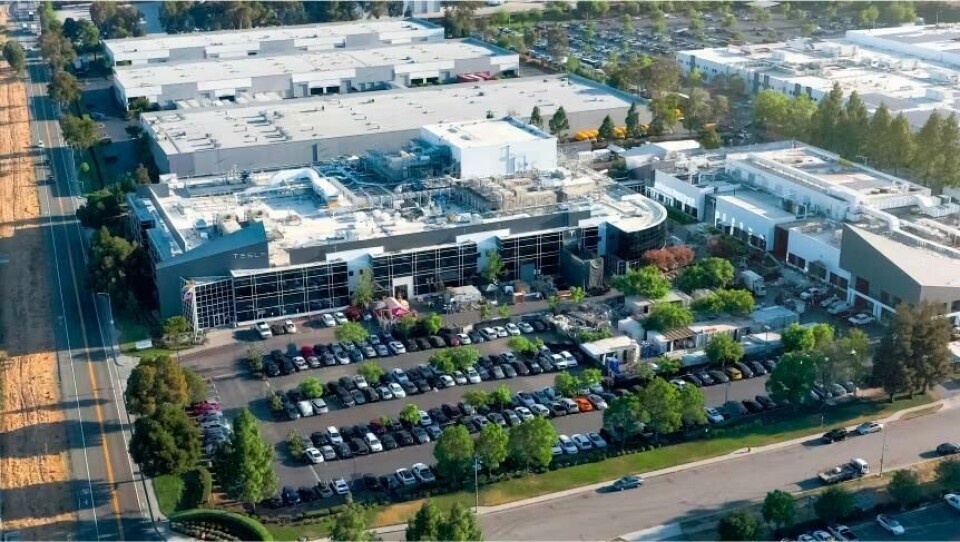

At the heart of Kato Factory’s operations lies the development and production of battery cells, modules, and packs tailored for Tesla’s EVs. This is the facility where Tesla pioneers the use of dry electrode technology; a departure from conventional lithium-ion battery production methods that rely on wet paste coatings for anodes and cathodes.
This particular innovation promises reduced energy consumption, streamlined factory space allocation, as well as lowered production costs. Since acquiring Maxwell Technologies in 2019, Tesla has been working on refining its dry electrode process. The facility both prototypes and manufactures battery cells, modules and packs, while also serving as a training ground for Tesla’s future battery production workforce.
Despite strides in battery technology (and tech in general), Tesla has been facing challenges in scaling up production of its 4680 battery cells, particularly with perfecting the dry coating process for cathodes. Sources said to be familiar with operations at Tesla’s Gigafactory in Austin, Texas, where the Model Y and Cybertruck are manufactured, have reported ongoing struggles to meet ambitious production targets due to technical hurdles in cathode manufacturing. Materials shortages are an ever-present risk for battery production.
Tesla aims to enhance its 4680 battery production capacity with plans to expand to eight production lines in Texas by late 2024. However, replicating operational success across multiple lines can present a formidable task, with initial scrappage rates expected to vary significantly until stability is achieved.
The complexity lies in efficiently mixing cathode materials—lithium, manganese, and nickel—with binders to form a cohesive layer on metallic foils without introducing moisture.
“Even as we approach the natural limit of cost down of our existing vehicle lineup, our team continues to focus on further cost reductions across all points of production, from raw materials to final delivery”
Tesla’s efforts to coat multiple strips of foil simultaneously to expedite production are hindered by challenges in maintaining uniform pressure and surface consistency, critical for battery electrode performance.
While Tesla works towards optimising its battery production processes, challenges in quality assurance persist, requiring robust data infrastructure and verification systems to identify and rectify production flaws. Despite setbacks, Tesla’s pursuit of dry-coated 4680 battery cells mark the company’s doggedness in tackling such challenges.
Gigafactory Nevada
Nestled in Storey County’s arid landscape, Gigafactory Nevada (also known as Gigafactory 1), plays a critical role in the company’s vision for sustainable energy. The sprawling suite near Lake Tahoe is a global leader in EV component and energy storage system production. With an annual capacity of 37 gigawatt-hours, the site has produced 7.3 billion battery cells, 1.5 million packs, and 3.6 million drive units, since early last year.
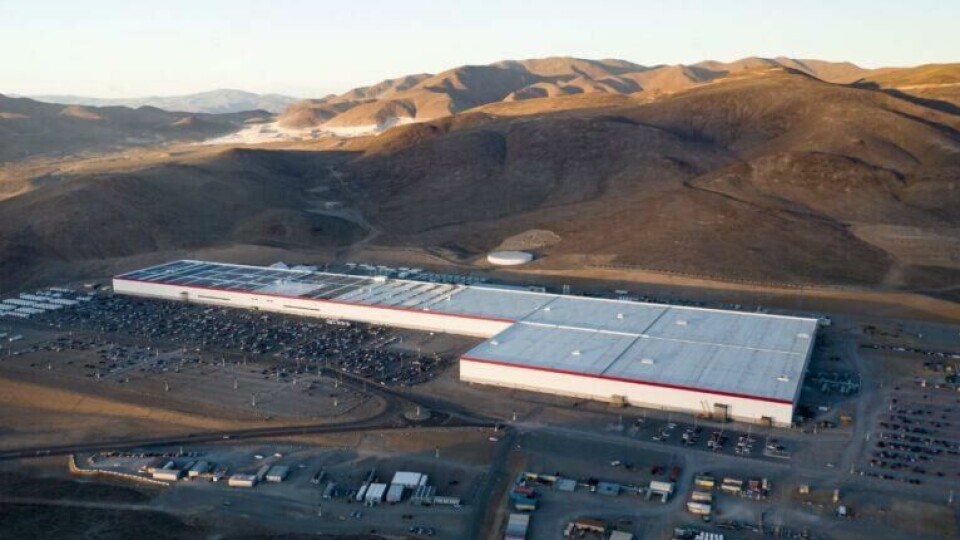

Then in January 2024, following the announcement of a $3.6 billion expansion plan a year prior, Tesla broke new ground at the site as part of its ambitious growth strategy.
The expansion includes the construction of a dedicated facility for manufacturing Tesla Semi electric trucks, alongside a new 100 GWh battery cell factory, aimed at the production of Tesla’s 4680 battery cells.
Named for their dimensions—46mm in diameter and 80mm in height—Tesla’s 4680 battery cells—store approximately 90 watt-hours of energy each, using standard lithium-ion chemistry. A Tesla Cybertruck battery pack, for example, integrates 1,344 of these cells, offering a total energy capacity of around 123 kWh.
Nevada aims to supply enough cells annually to power 2 million light-duty vehicles, according to Tesla. The expansion project, supported by $330 million in tax incentives from the state of Nevada over a decade, is expected to generate 3,000 new jobs, augmenting the current workforce of 11,000 at the site. Considering the obvious EV/sustainability crossover, Nevada is set to operate entirely on renewable energy sources, including solar, wind and geothermal power, furthering Tesla’s goal of achieving energy self-sufficiency while advancing renewable energy technology.
Gigafactory New York: Photovoltaics and AI supporting electrification
Gigafactory New York, also known as Gigafactory 2, is another cornerstone to Tesla’s EV production landscape. Although not directly involved in the battery production for Tesla’s EVs, the facility was established with substantial state investment to produce Solar Roof tiles, solar panels and electrical components for Tesla’s Supercharger network - a key infrastructure in the battery production web.
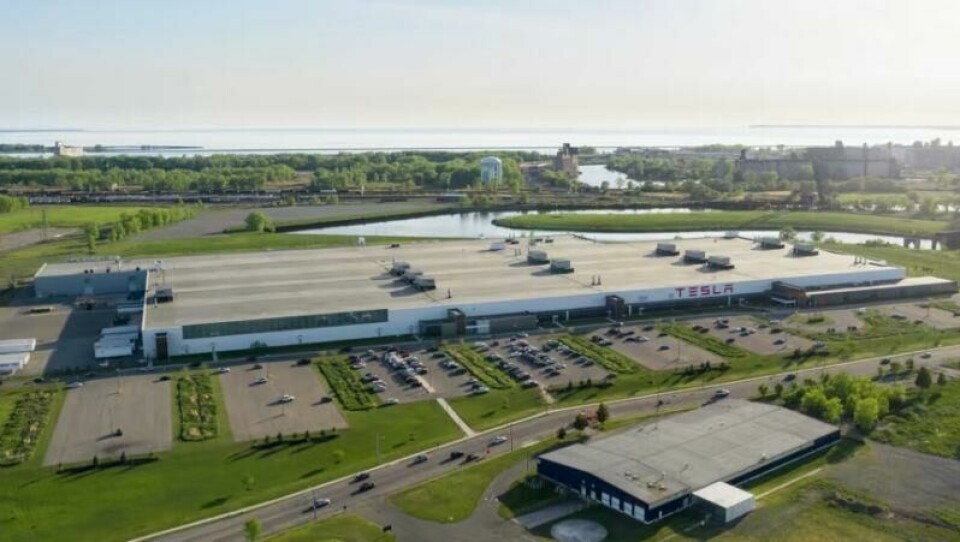

Despite initial challenges and shifts in production focus, including a transition away from solar panel manufacturing, Tesla is expanding operations to meet employment targets and enhance output efficiency. Gigafactory New York remains crucial to Tesla’s commitment to advancing clean energy and supporting its EV ecosystem.
In early 2024, the company also revealed plans for a substantial $500m project to establish the “Dojo” supercomputer cluster at Gigafactory New York. With a focus on computer vision the initiative is intended to bolster Tesla’s AI training efforts for its Full Self Driving technology and Optimus robot products. Battery and EV production abhor a vacuum.
Gigafactory Shanghai
Gigafactory Shanghai, (Gigafactory 3), holds a significant place in Tesla’s global manufacturing strategy as the company’s first production facility outside the United States. Situated in the Lingang Industrial Zone of Shanghai’s Pudong district, this advanced manufacturing plant has rapidly become a critical hub for Tesla’s EV production.
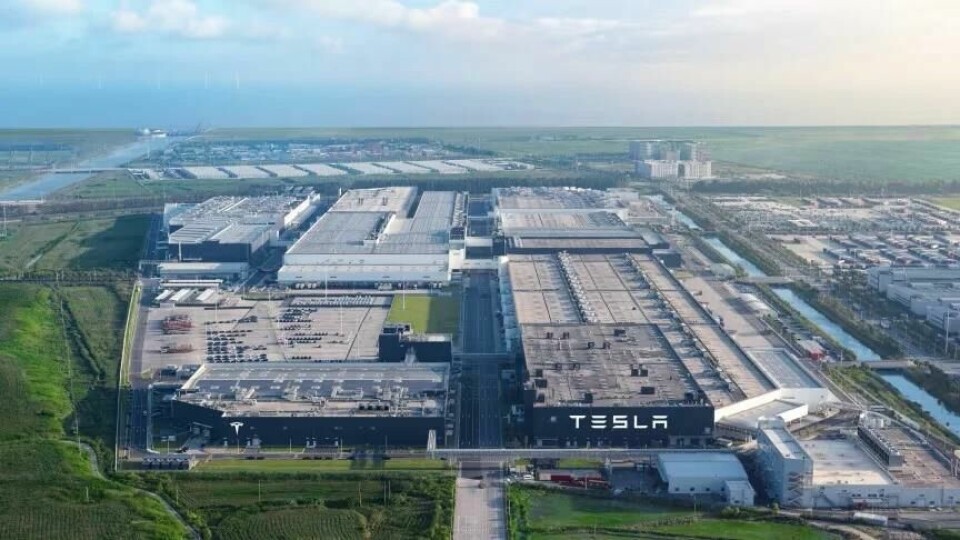

Construction of Gigafactory Shanghai commenced in January 2019, and remarkably, it began producing vehicles by October of the same year, showcasing Tesla’s ability to establish manufacturing capabilities swiftly in new markets.
The factory is primarily dedicated to producing two of Tesla’s most popular models: the Model 3 sedan and the Model Y crossover SUV.
By July 2023, Gigafactory Shanghai achieved an impressive annual production capacity exceeding 750,000 vehicles.
This high output has positioned the factory as Tesla’s primary production site for vehicles exported to regions without their own Gigafactory, highlighting its integral role in Tesla’s global supply chain. Beyond its production numbers, Gigafactory Shanghai represents a significant milestone in China’s automotive industry. It is the first wholly foreign-owned car factory in the country, where Tesla operates without a joint venture with a Chinese company, diverging from the traditional requirements for foreign automakers in China. The efficiency and growth of Gigafactory Shanghai have been notable.
”Shanghai resumed normal rate production in Q4 [2023], rebounding from the scheduled downtime in Q3. Production of the updated Model 3 ramped to full speed in less than two months”
Production of the Model Y at the facility has been rapidly outpacing that of the Model 3, reflecting increasing demand for Tesla’s electric crossover. Currently, the factory produces approximately twice as many Model Ys as Model 3s, aligning with Tesla’s global sales strategy and consumer preferences.
In the third quarter of 2023, Gigafactory Shanghai played a pivotal role in Tesla’s global operations, accounting for over half of the company’s worldwide deliveries. During this period, the factory produced 222,517 vehicles out of Tesla’s total global deliveries of 435,059, highlighting its important position in Tesla’s production ecosystem.
Alongside its successes, Gigafactory Shanghai has encountered challenges, including production disruptions attributed to upgrades and preparations for new model launches. For instance, in September 2023, the factory experienced a 12% decrease in deliveries compared to the previous year due to upgrades for the launch of the new Model 3.
Gigafactory Shanghai remains fundamental to Tesla’s manufacturing strategy, as it continues to expand its global footprint. The facility exemplifies Tesla’s ability to rapidly establish and scale production in key markets, while adapting to local conditions and evolving consumer demands.
Gigafactory Berlin—Brandenburg
Tesla’s Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg; the company’s inaugural, and newest manufacturing site in Europe, is a key achievement in Tesla’s global EV battery production expansion. Situated in Grünheide, Germany, approximately 35km southeast of Berlin, this cutting-edge facility is dedicated to producing the Tesla Model Y for the European market.
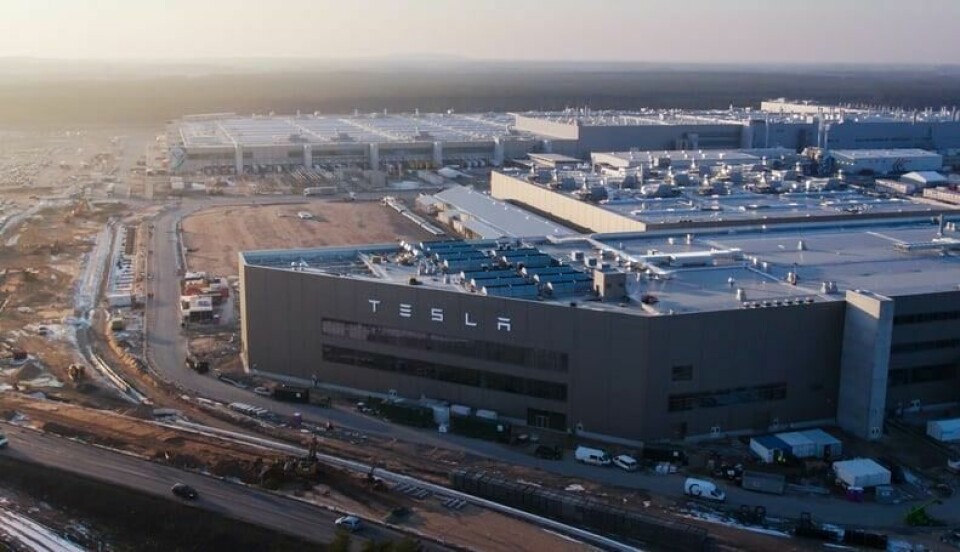

Commencing production in March 2022, Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg has swiftly scaled its operations, achieving a milestone output of 5,000 Model Y vehicles per week by March 2023. With an investment totaling around €4bn ($4.353m), the factory ranks among the world’s most efficient automotive plants. Tesla has streamlined production to assemble a Model Y in just 10 hours, contrasting sharply with the 30-hour timeline typical for comparable models from German manufacturers.
Beyond the Model Y, Tesla has ambitious plans to expand Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg’s capacity to approximately 1m units annually. This expansion aligns with the introduction of Tesla’s next-generation model, anticipated to be priced around €25,000 ($27,250). Furthermore, the facility aims to manufacture batteries, battery packs, and powertrains for Tesla vehicles in the near future. Despite its technological prowess, Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg has encountered challenges since its inception.
“Model Y production in Berlin [in early 2024] was down sequentially due to impacts from the Red Sea conflict and the arson attack that impacted the factory”
The factory has faced protests and instances of arson from environmental groups concerned about its impact on the local ecosystem, particularly regarding water usage and deforestation.
Nevertheless, despite such challenegs, Tesla remains resolute in its drive towards bolstering the Berlin-Brandenburg Gigafactory; it’s pioneering European hub, with future plans for production line expansions and output capacity enhancements.
Gigafactory Texas
Located in Austin, Gigafactory Texas (or Gigafactory 5) serves as Tesla’s strategic hub for EV production, focusing on the Model Y compact SUV and the high-profile Cybertruck. Cybertruck production commenced with pre-production models in July 2023 following long anticipation, followed by full-scale manufacturing in November of the same year, initially targeting markets exclusively within North America.
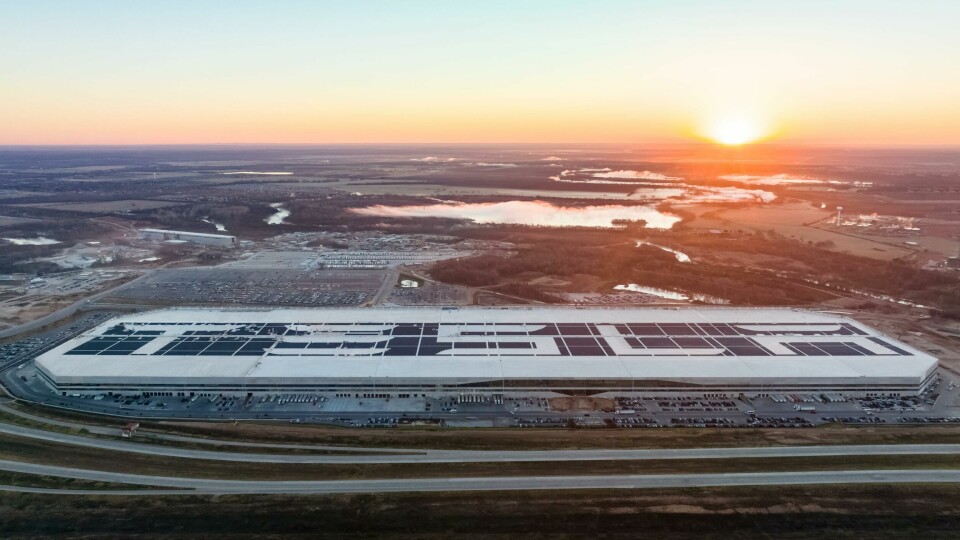

Giga Texas has already achieved its milestone of producing 5,000 Model Y vehicles per week, equating to an annual production capacity of around 250,000, and is now said to be showing signs of a significant ramp-up in Cybertruck production.
Despite automotive production sometimes being a somewhat secretive affair, in early January of this year, a drone operator and longtime Giga Texas enthusiast, Joe Tegtmeyer, captured early morning footage of the facility, showcasing numerous Model Y units and Cybertrucks. Tegtmeyer noted on (Musk’s own) X forum, that production of both vehicles appeared to be notably increased during the rare Sunday flight, highlighting a bustling outbound lot. The footage revealed approximately seventeen Cybertruck units (with an estimated count nearing 20) and several dozen Model Y units present at the time of filming.
Scheduled site upgrades paused Model Y production for a period of about 5 days in early July to ‘optimise’ manufacturing capabilities. To boot, Tesla’s application for an adjacent facility demonstrates a move towards vertical integration, potentially accommodating a site for the production of battery cathode materials. The expansion is also a sign of Tesla’s mission to enhance its supply chain efficiencies. Another noteworthy Giga 5 development is the sighting of The Boring Company’s Prufrock-3 tunnelling machine on-site, hinting at future underground infrastructure initiatives.
Tesla’s future focus: Gigafactory Mexico
Tesla has been working on plans for ‘Gigafactory Mexico’, which will come to be known as Gigafactory 6, near Monterrey, in the state of Nuevo León. Giga Mexico has been a topic of significant interest and speculation since its announcement in February 2023. The factory is expected to produce new Tesla models, including the much-anticipated affordable vehicle priced around $25,000, although Elon Musk has suggested that initial production of this model might begin in Texas before potentially moving to Mexico.
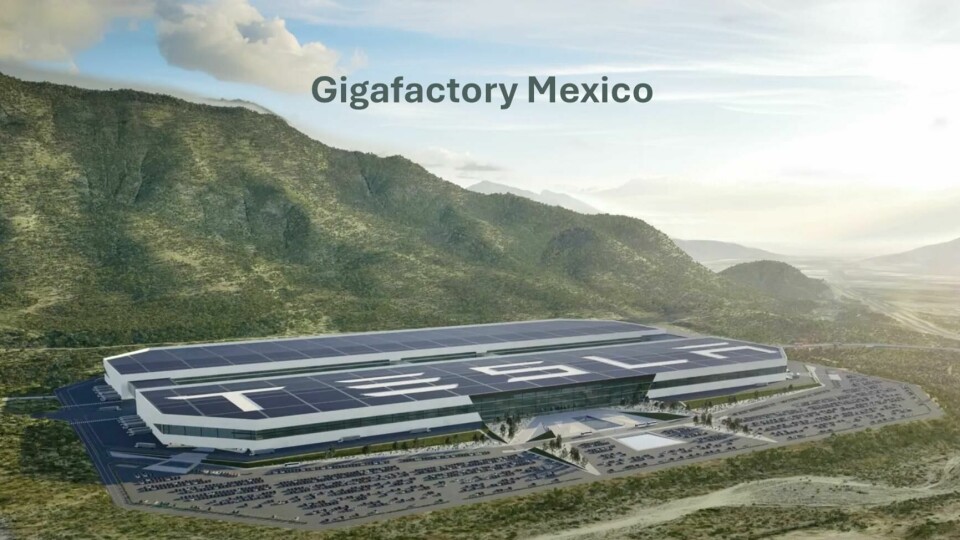

The huge undertaking, with an estimated investment of $10 billion, was initially slated to begin production as early as 2025, with the capacity to manufacture up to one million vehicles annually. Tesla’s reasons for building a Gigafactory in Mexico are numerous.
It’s part of Tesla’s strategy to reduce production costs, capitalise on Mexico’s strategic location near the US market and take advantage of trade benefits under the North American Free Trade Agreement. It also aligns with the broader trend of nearshoring, bringing production closer to end consumers.
The project has, however, faced numerous challenges and delays since its inception. The expected completion date has been pushed back from mid-2024 to 2025 - possibly 2026 - with some analysts suggesting it could be even later. These delays stem from a combination of factors, including global economic uncertainties, changing market conditions in the electric vehicle sector, and shifts in Tesla’s overall production strategy. Elon Musk has expressed caution about proceeding rapidly with the project, citing concerns about the global economy.
Despite the setbacks, both Tesla and the Mexican government remain committed to the project, with the state of Nuevo León offering substantial incentives, and the carmaker has secured all necessary permits, including environmental approvals, with the local government investing in infrastructure improvements to support the facility.