With automotive manufacturers faced with rapidly changing markets, Siemens discusses how they can transform variability on the shopfloor into predictable and executable production schedules

Based on the Digital Auto Report from PwC (available here), the total number of cars in use in Europe is forecasted to peak in 2025 and to decline thereafter. The number will continue to increase in China and at a slower pace in the US.
This market is driven by consumers and the demand for automation and electrification is growing fast, while the trend is to move from ownership to usership with digital buyers leading the way. A recent example of these trends comes from Volvo who announced that 100% of their vehicles will be electric by 2030, and be available online.
When we see all these trends arriving, we clearly imagine the new challenges car manufacturers and suppliers are anticipating. At the same time, standards and regulations are even more strict, which means manufacturers need to adopt sustainable manufacturing processes.
Increasing automation and electrification of new models means cars are becoming more complex to produce, with a growing Bill of Materials, especially considering the exponential growth in software and electronics components within a vehicle.
Also, with consumers moving from ownership to usership, mobility will be the new standard and car manufacturers need to reinvent themselves and their business models. And with stricter environmental standards and regulations manufacturers and suppliers need to adopt sustainable manufacturing processes.
Becoming lean and agile
In such a complex market scenario focusing only on efficiency and costs is clearly not enough. You need a compound mix of leanness and agility in that you must be lean to reduce waste and costs, but also be agile to positively face the big trends and upcoming challenges.
Companies adopting agile manufacturing have often already successfully implemented Lean manufacturing strategies, but want they now want to adopt agile concepts, to differentiate themselves from competitors in terms of quality and flexibility.
Lean and agile are not opposite approaches, but complementary for a successful manufacturing strategy that you must embrace to stay competitive in automotive market. Automotive manufacturing industry is one of the most complex environments where lean and agile manufacturing cooperate and integrate. Lean manufacturing helps manufacturers (in particular suppliers) to have more efficient production, reducing lead time and decreasing costs, while agile manufacturing allows automotive manufacturers to focus on customer demand and flexibility. It is a balanced and comprehensive approach, which often relies on planning and scheduling software solutions to achieve common goals.
Lean and agile at a glance:
Lean and agile enables manufacturers to:
• Optimise customer service
• Facilitate demand-driven production
• Accelerate product time-to-market
• Decrease operating costs
Allowing:
• Synchronisation
• Optimisation
• Responsiveness and visibility
• Integration and navigation with the information system
According to analysts, automakers and suppliers that do not want to sit out the industry transformation should do the following: Put agility as first priority; launch products faster; learn and adapt faster. They recommend focusing on capacity management and using market intelligence (demand dynamics, supply chain dependencies, shopfloor reality, etc.) and analysis to manage production on a day-by-day basis, and production scheduling can play a big role in this.
APS is part of the solution
Launch Fast, Learn Fast, Adapt Fast means that you must know quickly what needs to be produced and when. But how do you manage your production scheduling? Do you still rely on spreadsheets?Keeping track of production plans and schedules on the spreadsheets that different departments update manually can easily become a chaos. Spreadsheets will multiply while each department wants to keep track by its own one and then it is very hard to re-aggregate everything in a common plan. As spreadsheets don’t offer much in the way of integration possibilities, keeping track of production data and keeping your schedule aligned is extremely time consuming, it is very likely that by the time you get all information it’s out of date.
Even if you don’t rely on spreadsheets, having a planning and scheduling system that is not connected to real-time production data is like driving with an old generation navigation system; if something unexpected happens, your plan can not be achieved.
That’s the reason why best-in-class APS (Advanced Planning and Scheduling) uses real-time production data to update and synchronise scheduling. APS make use of a digital twin of your plant (the scheduling model) and historical + actual data from shopfloor to analyse, predict and synchronise plant supply and demand.
There are a number of key opportunities a better approach to scheduling can offer, such as leverage on innovative manufacturing technologies and process managed environments to achieve alignment and coordination between process planning and manufacturing execution. Also, synchronised and closed loop process between customer orders, production scheduling, and manufacturing execution. Implementing APS functionalities can enable supply chain coordination, enhancing collaboration and visibility.
The APS solution can support a manufacturer in managing the availability and synchronisation of limited and complex resources, such as labour, equipment, material and test devices, combined with more complex constraint types, to address the increasing need of more complex and accurate processes. It can also enable flexible production planning and workflow management, supporting the integration of more flexible machines, progressive implementation and allowing a company to gradually evolve skills and processes in order to fully exploit their potential, i.e. new technologies like Artificial Intelligence, to bring predictivity in schedule optimisations.
The solution is Opcenter APS
• Supporting scheduling rules that can be further customised for each application.
• Manual or automatic update for operation production status
• Schedule re-calculation
• Can be easily Integrated with ERP and MOM systems
• Natively Integrated with SIEMENS MOM products and SIEMENS PLM products in the Closed Loop Manufacturing integration concept.
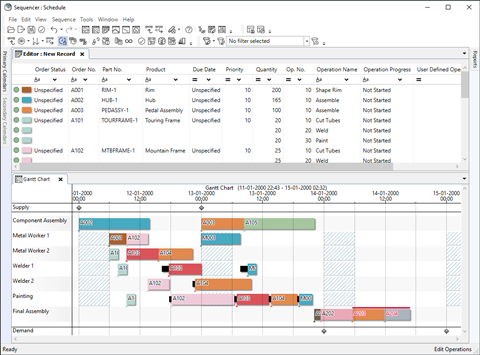
Different use cases for Opcenter APS in the automotive industry
Production scheduling in a machining job shop
Challenges:
• Machining job shop is a high mix and variable volume manufacturer. The challenge in such an environment is to manage variable and complex routing, complex machine setup, versatility of resources capabilities (machines and human resources), constraints for material and energy saving, while keeping WIP within acceptable limits and resource utilisation at a proper level.
Benefits:
• Multiple constraints management; constraint model differentiation per machine types; overall setup minimisation (trough sequence dependent setup calculation and grouping criteria); lead time reduction thanks to customer specific priority management.
• Bottlenecks are visible clearly over the timeline and Opcenter APS offers scheduling rules to enhance their throughput. Staff/tool availability and staff skills and versatility can be easily managed as secondary constraints.
• Planned maintenance (for machines and tooling) can be considered and included in production planning in order to properly schedule maintenance based on customer and machine/tool specific maintenance plans.
• Great visibility and transparency to find out the root cause of violated due dates and allow planners to easily adjust shift plans, capacities of machines, availability of personnel to solve due date problems.
Production scheduling of parts manufacturing
Challenges:
• Keeping stock levels low and provide Just-In-Time delivery. Capacity definition and adjustment is crucial in this context. A usual challenge for planning and scheduling parts in automotive FTS is also to adjust batch/lot size to keep some flexibility at schedule level without degrading the productivity due to too many machine setup.
Benefits:
• Priority management, locking options with detailed constraint model to ensure just in time delivery.
• Grouping rule with customer specific criteria for lot/batch size adjustment to ensure high effectiveness and low setup time.
• Material explorer for visibility on material consumption, projected stocks and shortages. Material pegging rules allowing allocation of material intelligently many times during the day even to manage changed order quantities and due dates.
• Flexible constraint model to adapt to different types of processes.
• Flexible calendar module to model any type of capacity model (machine and human).
Scheduling of testing environments
Challenges:
• The challenge for planning and scheduling in the test environment is the availability and synchronisation of limited and complex resources. Personnel, equipment, material and test devices availability combined with more complex constraint types, such as test duration, determines the capacity of your facility.
Benefits:
• Priority management, locking options with detailed constraint model to ensure just in time delivery.
• Grouping rule with customer specific criteria for lot/batch size adjustment to ensure high effectiveness and low setup time.
• Material explorer for visibility on material consumption, projected stocks and shortages. Material pegging rules allowing allocation of material intelligently many times during the day even to manage changed order quantities and due dates.
• Flexible constraint model to adapt to different types of processes.
• Flexible calendar module to model any type of capacity model (machine and human).
Siemens Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) software, Opcenter is a holistic solution that enables you to implement your strategy for the complete digitalisation of manufacturing operations. Our portfolio provides end-to-end visibility into production allowing decision makers to readily identify areas to be improved within both the product design and associated manufacturing processes, and make the necessary operational adjustments for smoother and more efficient production.
Our products provide solutions for:
• Advanced planning and scheduling
• Manufacturing execution
• Quality management
• Manufacturing intelligence
Find out more here